Java Arrays
Java Arrays
Introduction
In Java, an array is a data structure that allows you to store multiple values of the same type. It provides a convenient way to organize and manipulate collections of data.
Declaration and Initialization
To declare an array in Java, you specify the type of the elements followed by the array name:
type[] arrayName;For example, to declare an integer array:
int[] numbers;Arrays can be initialized in two ways:
- Using the
newkeyword:
arrayName = new type[arraySize];type[] arrayName = {value1, value2, ..., valueN};Accessing and Modifying Elements
Array elements are accessed using their index, which starts at 0. You can use the index in square brackets [] to access or modify an element:
// Accessing elements
type element = arrayName[index];
// Modifying elements
arrayName[index] = newValue;Array Length
You can obtain the length of an array using the length property:
int size = arrayName.length;Iterating over an Array
Looping constructs like for or foreach can be used to iterate over the elements of an array:
// Using a for loop
for (int i = 0; i < arrayName.length; i++) {
// Process array element
}
// Using a foreach loop
for (type element : arrayName) {
// Process array element
}One Dimensional(1 D)
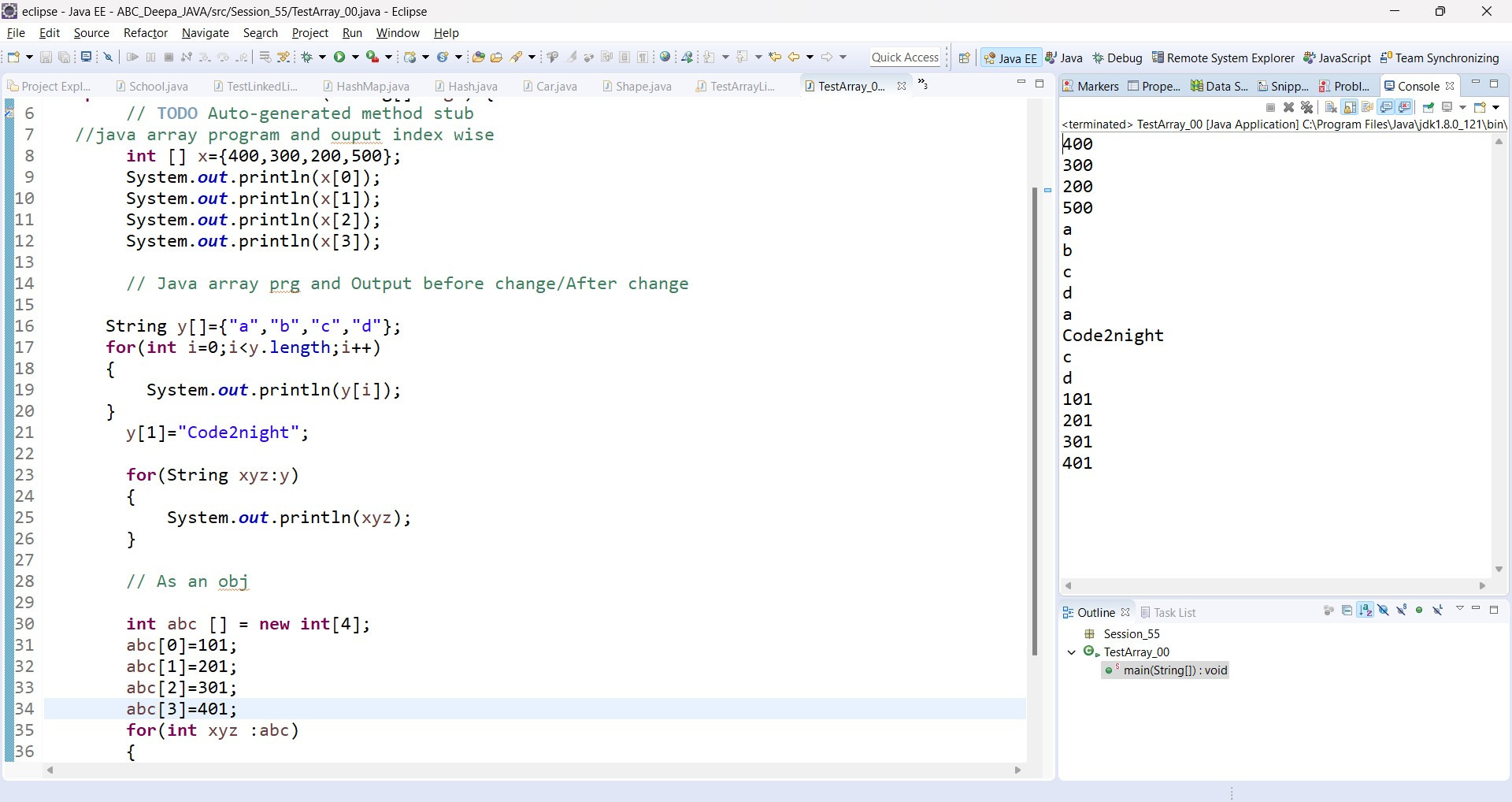
//java array program and ouput index wise
int [] x={400,300,200,500};
System.out.println(x[0]);
System.out.println(x[1]);
System.out.println(x[2]);
System.out.println(x[3]);
// Java array prg and Output before change/After change
String y[]={"a","b","c","d"};
for(int i=0;i<y.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(y[i]);
}
//-----After Change
y[1]="Code2night";
for(String xyz:y)
{
System.out.println(xyz);
}
// As an object
int abc [] = new int[4];
abc[0]=101;
abc[1]=201;
abc[2]=301;
abc[3]=401;
for(int xyz :abc)
{
System.out.println(xyz);
}Conclusion
Java arrays are a fundamental part of the language, allowing you to store and manipulate collections of data. Understanding how to declare, initialize, and work with arrays is crucial for Java developers.